- Company
- Products
- Technical report
- Indusrial cleaning
- Micro Joining and Assembly Technology
- Ultrasonic technology
- Trouble solution
- Cleaning
- Removing
- Attaching
- PCB Columns
Published on :
Recently, conductive adhesives/silver pastes have been attracting attention, but if used incorrectly, they may not provide sufficient performance.
This page explains how to use conductive adhesives, using the thermosetting type and the dry type as examples, and introduces the procedures of [thawing], [cleaning], [applying], and [curing], as well as points to be aware of.
As the name suggests, conductive adhesives are adhesives that conduct electricity. They contain silver as an electrically conductive component and are sometimes referred to as silver paste or silver adhesive.
Since they can bond to metals and resins that cannot be soldered, they are used in a variety of applications. In recent years, as more and more products are made of films and resins with low heat resistance, their use is expanding as a means of conductive adhesion in place of solder.
This page introduces the use of conductive adhesives (silver paste), using the TK PASTE series of conductive adhesives developed by KAKEN TECH as an example.
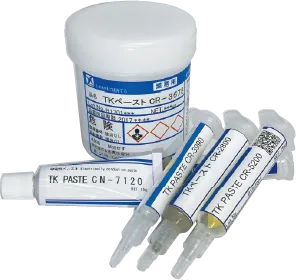
This is a type of conductive adhesive that bonds through a resin curing reaction caused by heating. They are called "heat curing type". Among conductive adhesives, this type has high adhesive strength and good conductivity.
Typical types are those using epoxy resins, which also have excellent heat resistance. For components that can be heated to about 100°C, we recommend the epoxy heat curing type.
| Product # | CR-2800 | CR-5200 | CR-3520 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Features | Low temp. curing | Low temp. curing good conductivity |
Good heat resistance |
| Usage | Grounding Shielding |
Adhesion of electronic components |
Die attaching |
| Binder | Epoxy | Epoxy | Epoxy |
| Specific resistivity | 6×10-3Ω・cm | 2×10-4Ω・cm | 4×10-5Ω・cm |
| Heat transfer characteristics | ― | ― | 20W/m・K |
| Curing condition | 90℃×60分 | 100℃×60分 | 130℃×30分+ 180℃×60分 |
| Storage condition | Frozen(-10℃以下) | ||
| Package | 10g(5cc) syringe |
10g(5cc) syringe |
5g(3cc) syringe |
 |
[Thawing] Thaw the frozen conductive adhesive. Leave the container tightly closed at room temperature for at least 30 minutes to thaw. Wipe off any water droplets on the container before opening. | |
|---|---|---|
 | Thawing is done at room temperature. Forced heating such as hot water, warm water, hot plates, ovens, hair dryers, etc. may cause the container to heat up rapidly and burst. | |
 | Be careful not to allow condensation from thawing to get into the adhesive. If the lid or cap is opened first, condensation may get into the container and make the adhesive unusable. | |
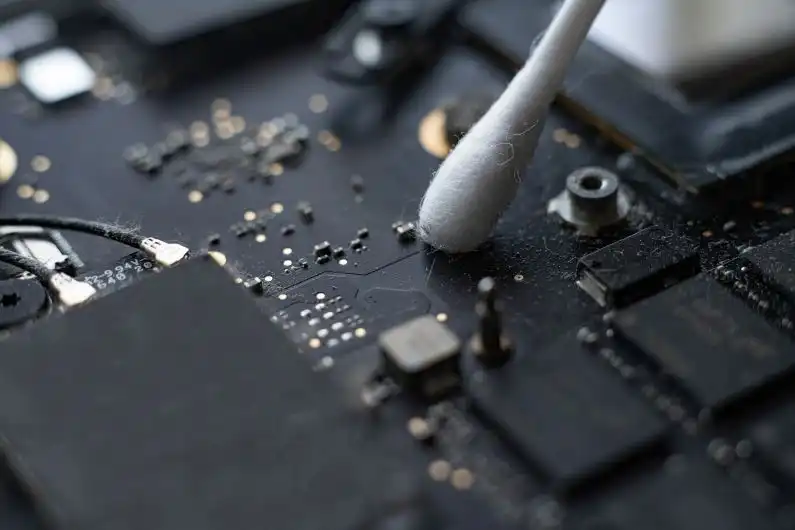 |
[Cleaning] Clean the area to be applied adhesive with alcohol or acetone. If flux or oil remains on the surface, sufficient conductivity and strength cannot be obtained. | |
 | Allow the cleaning agent to dry completely. If the cleaning agent remains on the area to be applied, the adherend may not adhere properly. | |
 |
[Applying] Apply the correct amount without excess or deficiency. Use a dispenser for accurate application. | |
 | The inner diameter of the needle used should be appropriate for the adhesive. If it is too small, it may cause clogging. | |
 | Immediately after application, cure the product in a thermostatic oven. If the adhesive is left to cure for too long after application, it may not be cured properly and sufficient performance may not be obtained. | |
 | The temperature and humidity of the working environment may affect performance. Working temperature of 25°C or lower is desirable. | |
 |
[Curing] Heat curing type conductive adhesives are made conductive by heat curing. Heat the adhesive in a thermostatic oven under the recommended curing conditions set for each adhesive. | |
 | For heating, use a thermostatic oven that can maintain a constant temperature. Hot plates, hair dryers, etc. do not heat uniformly and may not provide sufficient performance. | |
 | Curing conditions vary depending on temperature, time, amount applied, and quantity put into the oven. The most common problems in using conductive adhesives are caused by improper curing conditions. It is important to experiment in advance with the actual equipment and materials to determine the optimal curing conditions. | |
Drying type conductive paste becomes conductive when the solvent component in the paste volatilizes, dries, and solidifies.
Compared to the heat curing type, the bonding strength is not as high, so it is often used in conjunction with other bonding methods such as screw fixing.
Since it can be used at room temperature, it is suitable for use on items that are not extremely heat resistant.
| Product # | CN-7120 | CN-7122S | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Features | Room temp. drying | Dry slowly | ||
| Usage | Ground Shielding |
|||
| Binder | Thermoplastic resin | |||
| Specific resistivity | 5×10-4Ω・cm | |||
| Heat transfer characteristics | ― | |||
| Drying condition | Set temp. | Estimated drying time | Set temp. | Estimated drying time |
| 25℃ | 60分 | 25℃ | 120分 | |
| 40℃ | 10分 | 40℃ | 20分 | |
| 60℃ | 5分 | 60℃ | 10分 | |
| Storage condition | Frozen(-10℃以下) | |||
| Package | 15g aluminum tube/td> | |||
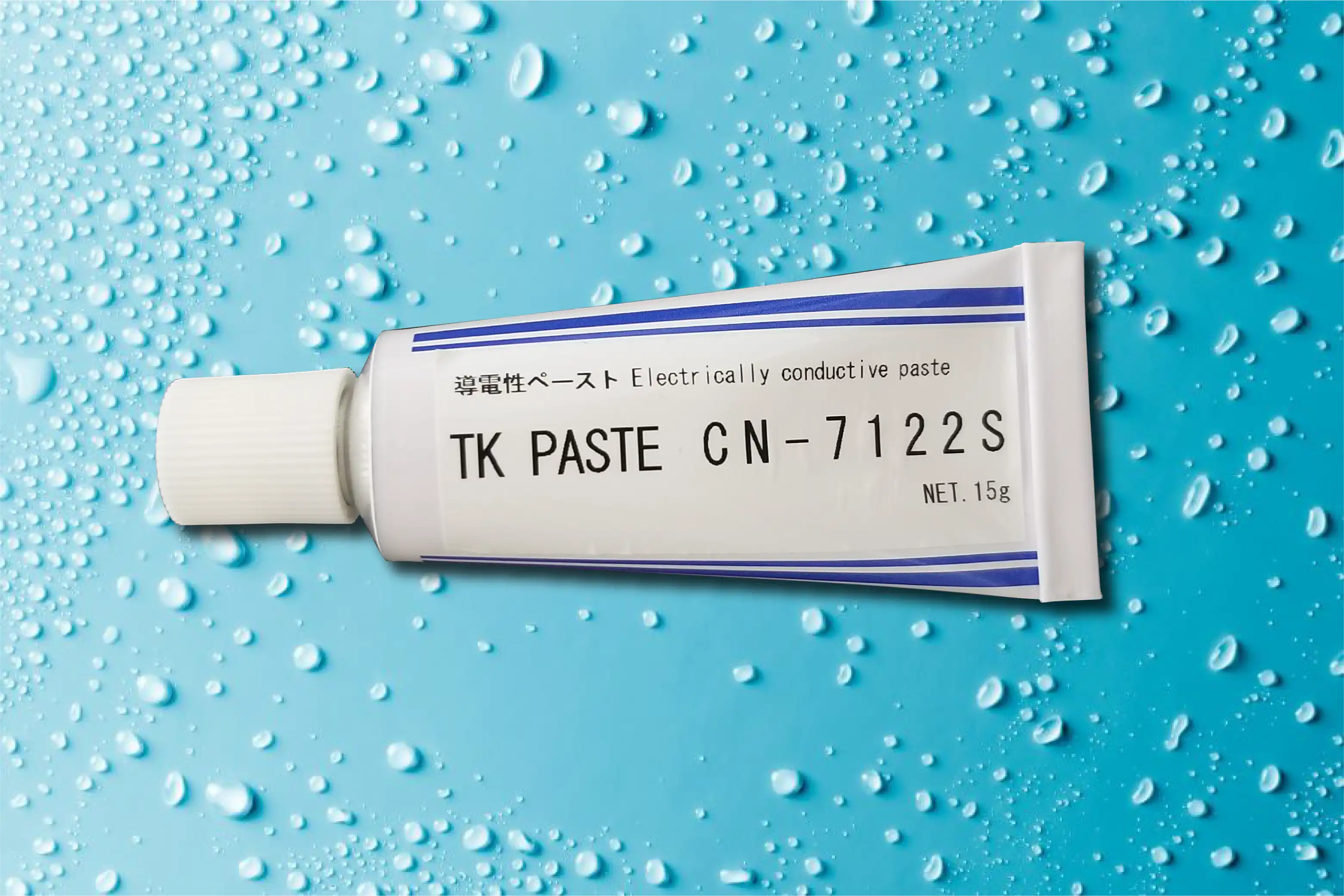 |
[Thawing] Thaw the frozen conductive adhesive. Leave the container tightly closed at room temperature for at least 30 minutes to thaw. Wipe off any water droplets on the container before opening. | |
|---|---|---|
 | Thawing is done at room temperature. Forced heating such as hot water, warm water, hot plates, ovens, hair dryers, etc. may cause the container to heat up rapidly and burst. | |
 | Be careful not to allow condensation from thawing to get into the adhesive. If the lid or cap is opened first, condensation may get into the container and make the adhesive unusable. | |
 |
[Cleaning] Clean the area to be applied adhesive with alcohol or acetone. If flux or oil remains on the surface, sufficient conductivity and strength cannot be obtained. | |
 | Allow the cleaning agent to dry completely. If the cleaning agent remains on the area to be applied, the adherend may not adhere properly. | |
 |
[Applying] Apply the correct amount without excess or deficiency. Use a dispenser for accurate application. | |
 |
The inner diameter of the needle used should be appropriate for the adhesive. If it is too small, it may cause clogging. | |
 |
Immediately after application, cure the product in a thermostatic oven. If the adhesive is left to cure for too long after application, it may not be cured properly and sufficient performance may not be obtained. | |
 | The temperature and humidity of the working environment may affect performance. Working temperature of 25°C or lower is desirable. | |
 |
Drying type conductive pastes obtain conductivity by volatilizing the solvent component. Use a thermostatic oven and dry under the recommended conditions. | |
 | For heating, use a thermostatic oven that can maintain a constant temperature. Hot plates, hair dryers, etc. do not heat uniformly and may not provide sufficient performance. | |
 | Drying conditions vary depending on temperature, time, amount applied, and quantity put into the oven. The most common problems in using conductive paste are caused by improper drying conditions. It is important to experiment in advance with the actual equipment and materials to determine the optimal drying conditions. | |
②Open the head cap.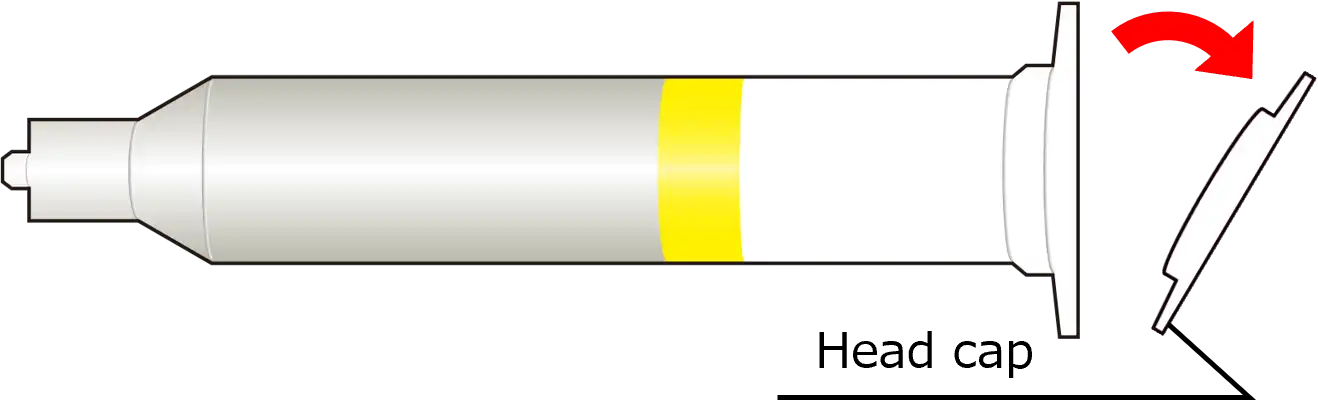 |
| ③Open the needle cap by turning it counterclockwise. Note that paste will be dispensed if the needle cap is opened before the head cap.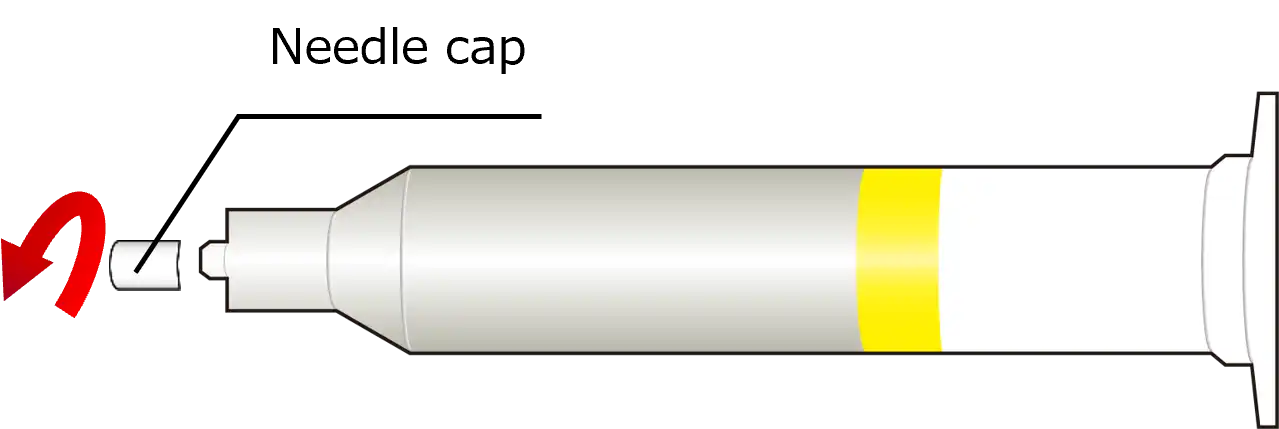  |
| ④Install the needle and set it in the dispenser. |
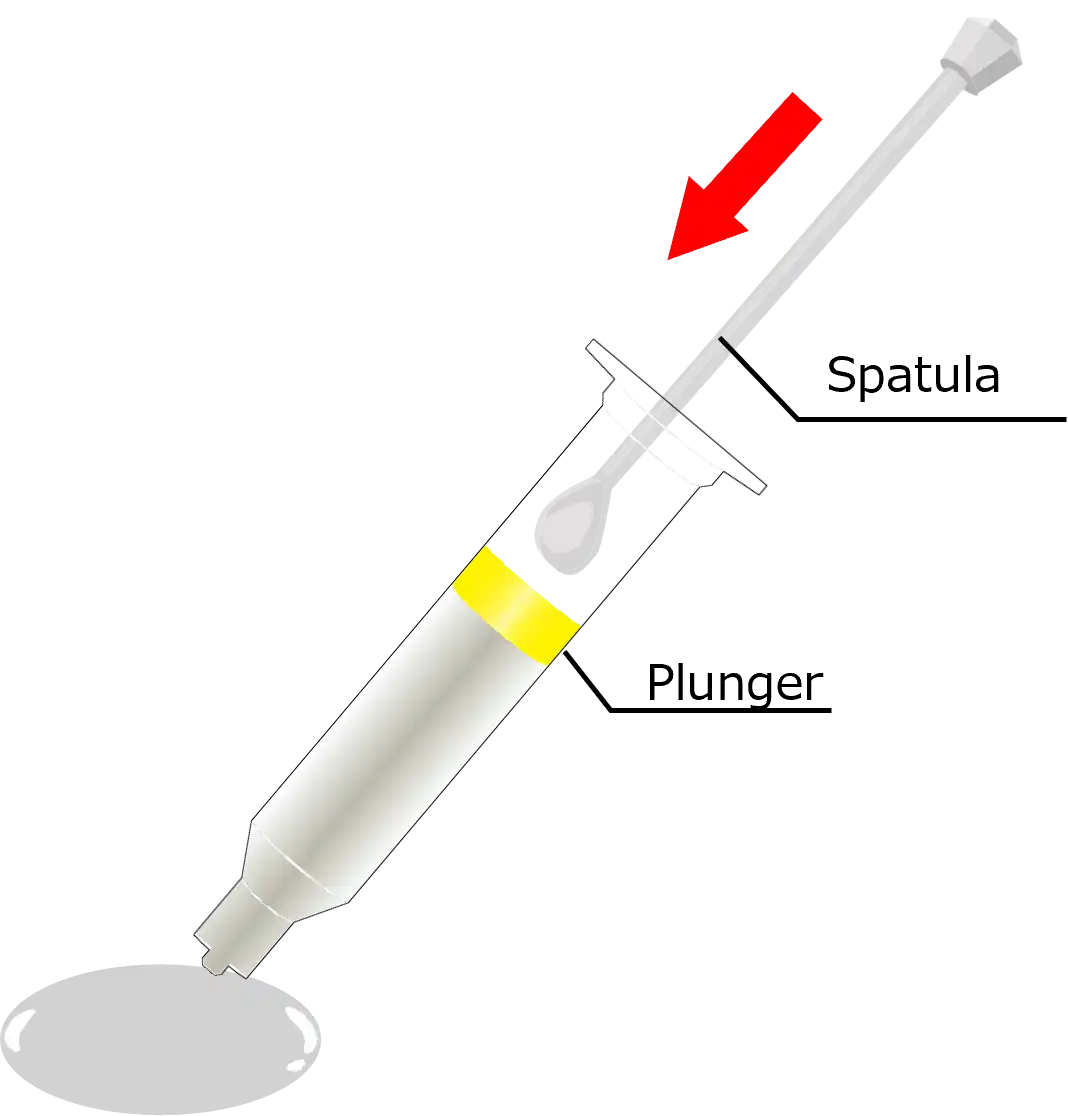 *Do not remove the yellow plug (plunger). *Please note that when applying without using a dispenser, it will be difficult to dispense the paste if a needle is attached. |
 |
Trouble solution
|
|---|---|
 |
Trouble solution
|
 |
Products information
|
| Inquiry |